Normally, after long and heated planning meetings, new strategies are conceived and rolled out. Most of these strategies are set with “fact and figures” in mind. We hear the following initiatives being rolled out: increase the net sales by 8%, reduce the costs by 2.3%, reduce production waste by 1.0%, just to name some examples.
Forgetting that in order to achieve these goals, employees at all levels of the organization, must poses and harness mindset skills that will support their implementation. Strategies overlook the employee’s individual personal traits, as well as the acquired knowledge and skills that impact and contribute to the macro and micro-systems in which they interact.
Therefore, emotionally intelligent abilities and skills are becoming increasingly significant in topics ranging from leadership, team building, communication and performance. The promotion of such capabilities has proven to have a direct impact on the execution of a business strategy, the completion of top and bottom-line objectives and the overall productivity of a company.
With this in mind, I defined a guideline which considers the emotional intelligence behavioral components needed to achieve the proposed strategical objectives and the learning tools needed to enhance them. I departed from the assumption that the technical skills are in place and that support must happen strictly on the behavioral skills of the employees. The guideline is then followed by an example.
Guideline
- Define the strategy
- Define emotional competences needed to the support strategy
- Breakdown of goal into tasks and skills at team and manager level
- Assess employees for emotional intelligence competences with EQ Tool
- Tackle gaps between emotional competences/skills and projected goal
- Create integrated development plans (IDPs) based on coaching, e-learning and blended learning courses
Breaking down a strategy: A practical example
Strategy definition
The strategy is to increase net sales by 8%, by tactically targeting consumers with relevant online promotions. To do so, the data quality of the consumers database must be improved, especially data containing emails and phone numbers must be updated. The teams involved are the customer service team, the marketing team and the IT team. (For exemplary and simplification purposes I will focus exclusively on the customer service team).
Definition of emotional competences
Employees must harness emotional competences that support effective communication skills. How will the customer service team members will communicate verbally with the consumers?
Consequently, the emotional intelligence competences selected to develop are: assertiveness, empathy, conflict resolution and self-control.
Breakdown of goal into tasks and skills
Customer service team tasks: Contact telephonically consumers with incomplete profiles, if the customer agrees to give email address and phone number, they will receive a 10% discount on their next purchase.
Customer service team skills: In order to successfully get information form consumers, the customer service team must communicate in an assertive and empathic way, always projecting self-control.
Assess employees with EQ-i 2.0 Model
Employees will be assessed using the EQ-i 2.0 Model of Emotional Intelligence. The assessment tool is a scientifically validated methodology that supports the development of the 5 distinct aspects of emotional and social functioning: Self-perception, Self-expression, Stress Management, Decision Making and Interpersonal skills (see Figure 1). The tool is administered online. As depicted on Figure 1, the model supports the enhancement of 15 sub scales of Emotional Intelligence skills which are critical to workplace success.
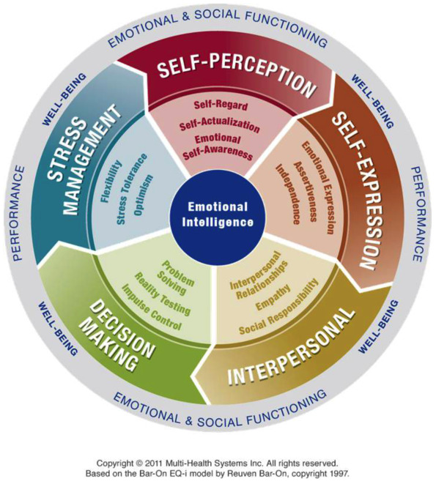
Tackle gaps
As seen on Figure 1 assertiveness, empathy and impulse control are part of the 15 subscales that are measured by the model. Based on the team and individual results, a plan to enhance and further develop these specific competences is detailed. This is done by creating by IDPs which include coaching, e-learning and blended learning activities.
Create integrated development plans (IDPs)
To harness the behavioral skills needed to support the strategy, the customer service team members were required to complete an (1) e-learning module covering the theory and definitions of each competence as well exemplifying situations in which phone calls reflected assertive and empathic behaviors. The second step (2) was to complete instructor led trainings (ILT) in which empathic, controlled and assertive communication with clients was practiced. The ILT was supported by a 3-week challenge in which participants were required to practice each component in a real-life situation. Coaching sessions were organized for team members which rated 90 or below on the individual competences (assertiveness, empathy and self-control). These sessions supported an in-depth development of the behavioral skills needed to achieve the strategy.
After the completion of the e-learning, ILT trainings and coaching series, participants were reassessed to measure their improvement against the objectives set. Finally, a report recommending best practices was delivered.
Conclusion
Next time when attending strategic planning meetings or writing down your team strategies and objectives reconsider if employees hold the right behavioral skills needed to complete them. Assessing their emotional intelligence competences and boosting them can signify the make or break of the proposed strategy.
FURTHER REPRODUCTION PROHIBITED WITHOUT PERMISSION

